Natural Killer Cells (NK cells) is an important immune system component. The function of NK cells is to kill cells infected with viruses or that otherwise present abnormal antigen. Natural Killer cells were discovered in 1973 by two different research groups who identified the NK cell lineage in mice. NK cells are a form of white blood cell which patrol our body searching for cells to kill. They do this due to their ability to recognize foreign or abnormal cells that have been infected with a virus or bacteria and then kill the infected cell.
Another type of white blood cell called B-cells produces antibodies, but these are found in our blood and not our lymph system. It’s important to consider cell division because it is a major factor in developing cancerous tumors. Natural killer cells serve as the body’s first line of defense against infected cells, especially cancerous cells. It is estimated that 30% of all cancers can be attributed to the loss of Natural killer cells. This makes natural killer cells a critical player in cancer prevention and suppression.
What are Natural Killer Cells?
Natural killer cells (NK cells) are part of the inborn branch of the immune system. Natural Killer cells are thought of typically as sentinels that patrol body tissues and act as first responders. The natural killer cells look for abnormal cells; natural killer cells can kill these abnormal cells even if they haven’t encountered or been sensitized to them before. Natural killer cells can recognize diseased cells through a process called antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC).
This means that they are effective initial responders as soon as an assault happens. For that reason, natural killer cells are very efficient at killing any cells that have been virally infected or become mutated through cancerous transformation. Killer cells are white blood cells that attack infected cells and tumor cells. They act as antibodies to help the human body fight against infections, parasite invasions, and cancer cell mutations. We would be looking at Cd11c Antibody, Cd14 Antibody, and Cd16 Antibody related to the immune system.
CD11c Antibody
CD11c Antibody has a size of 100 μg/vial. The Antibody has Mouse and Rat as reactive species with Rabbit as its host. CD11c Antibody is tested and compatible in ELISA, IHC-P, WB applications. The CD11c Antibody is of the Lyophilized form, contains in each of its vials 4mg Trehalose, 0.9 mg NaCl, 0.2 mg Na2HPO4, and is Polyclonal.
CD11c Antibody should be stored at -20°C for one year from the date of receipt.
After reconstitution, the Antibody must be stored at four °C for one month. The CD11c Antibody can be aliquoted and stored frozen at -20°C for six months. The Antibody should not be frozen or thawed repeatedly. CD11c Antibody validates all antibodies on WB, IHC, ICC, Immunofluorescence, and ELISA with positive and negative samples to ensure specificity and high affinity.
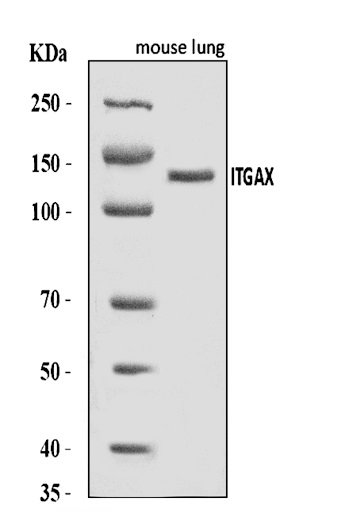
CD14 Antibody
CD14 Antibody reacts with these species Mouse and Rat. The Antibody has a size of 100ug/vial with Rabbit as its host species. The Antibody is tested and compatible in ELISA, Flow Cytometry, IHC-P, WB
applications. The CD14 Antibody has the Lyophilized form and is polyclonal, with each vial of the Antibody containing 4mg Trehalose, 0.9mg NaCl, 0.2mg Na2HPO4, 0.05mg NaN3.
CD14 Antibody has no cross-reactivity with other proteins and should be stored at -20˚C for one year from the date of receipt. After reconstitution, the Antibody must be stored at 4˚C for a month. The CD14 Antibody can be aliquoted and stored frozen at -20˚C for six months. You should avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. The Boster bio CD14 Antibody validates all antibodies on WB, IHC, ICC, Immunofluorescence, and ELISA with known positive and negative samples to make sure of specificity and high affinity.
CD16 Antibody
CD16 Antibody is tested in Direct ELISA, Flow Cytometry, IF, IHC-P, ICC, and has a size of 100μg/vial, with Humans as the reactive species and rabbits as the host. CD16 antibody is of the Lyophilized form, polyclonal in nature, and has each vial containing 4mg Trehalose, 0.9mg NaCl, 0.2mg Na2HPO4, 0.05mg NaN3. CD14 Antibody has no cross-reactivity with other proteins.
CD14 Antibody should be stored at -20˚C for one year from the date of receipt. After reconstitution, CD14 should be at 4˚C for one month. The Antibody can be aliquoted and stored frozen at -20˚C for six months. Repeated freeze-thaw cycles should be avoided with CD14 antibodies. CD14 Antibody validates all antibodies on WB, IHC, ICC, Immunofluorescence, and ELISA with known positive and negative samples to ensure specificity and high affinity.
Conclusion
Natural Killer cells may become central to cancer treatment and the possibility of fighting it. Although researchers are just starting to understand the potential of Natural Killer cells, the study of this cell type is expanding rapidly. It may hold significant promise for future treatments for cancer patients.